Reham Sharafeldin Osman Hajomer
U M S T, Sudan
Biography
Reham Sharfeldeen Osman has her expertise in evaluation and passion in research, search and discovery of natural drugs from plant origin. Her open and contextual evaluation model based on responsive constructivists creates new drugs for improving and treating of infectious diseases.
Abstract
Statement of the Problem: Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones [triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)] which is commonly caused by iodine deficiency. It is a potentially serious disorder and if left untreated it can lead to memory loss or mental slowing as well as depression and may become more severe over time. The current medical therapies for hypothyroidism are often deemed inadequate because of difficulties in regulating the level of thyroid hormones through use of conventional drugs. Herbal drugs have proven to be useful in number of diseases, and they have the capacity to cure such metabolic disorders synergistically at different steps. Therefore, more research must be done for effective and safer anti-hypothyroidism agent from plants. The purpose of this study is to know whether Lepidium sativum would affect the level of thyroid hormones.
Methodology: The extract was prepared by Soxhlet apparatus. The anti-hypothyroidism activity was tested using thirty male Wistar rats. They grouping into five groups, Group 1: Normal group=administered only distilled water. Then 10 mg/kg propylthiouracil was added to the drinking water of all other groups to induce hypothyroidism. Group 2: Negative control without any treatment; Group 3: Test group=treated with oral administration of 500 mg/kg extract; Group 4: Treated with oral administration of 250 mg/kg of the extract; Group 5: Standard group (positive control)=treated with intraperitoneal levothyroxine. All rats were incubated for 20 days at animal house with room temperature of proper ventilation provided with standard diet.
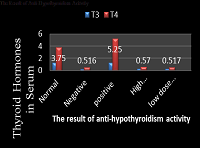
Findings: The results show that the L. sativum extract was found to increase the T3 and T4 in the propylthiouracil induced rats with values (0.29 ng/dl T3 and 0.57 U T4) for the 500mg/kg and (0.27 ng/dl T3 and 0.517 U T4) for the 250mg/kg in comparison with standard with values (0.241 ng/dl T3 and 0.516 U T4) so that L. sativum can be stimulatory to thyroid function and possess significant anti-hypothyroidism effect with p-values ranges from (0.000006*–0.893472).
Conclusion & Significance: L. sativum extract was found to possess anti-hypothyroidism effects and act as an agent that stimulates thyroid hormone secretion.
Recommendations: Further investigation should be carried to investigate the anti-hypothyroidism effect of L. sativum extract at the compound level.